

Russia’s defense industry is critically dependent on imported chemicals, catalysts, and chemical-technology equipment, an analysis by The Insider has found. The production of fuel for military aircraft and missiles, resins for detonators, and high-strength fibers for body armor is not possible without foreign catalysts and additives. China, India, and Iran help Russia circumvent international restrictions, providing Russian plants with chemical products, including those made by Western manufacturers.
Content
Foreign chemicals critical for missile production in Russia
Critical dependence on imported catalysts in petrochemicals
Western equipment for gas chemistry
Catalyst production: capacity fell short
Iranian assistance
Polymers: no catalysts for polypropylene and polyethylene
New industrial complexes for petrochemicals: smuggling or replication
Low-volume chemicals are more dependent on imports than bulk chemicals
Fuel additives: no domestic antistatic agents or additives
Suppliers of chemical equipment and catalysts
Where the Russian chemical industry stands in 2025
Foreign chemicals critical for missile production in Russia
Although Russia manufactures most of its defense products domestically using Russian raw materials, the technological chain features “weak links” — imported catalysts, plasticizers, additives, and components of chemical-technology equipment.
For example, missile and aviation fuel requires chemical transformations such as hydrotreatment, cracking, and reforming — all of which are based on catalytic processes.
For instance, the Decylin-M high-calorie fuel, which is used to power missiles of the Oniks, Kalibr, and Kh-101 varieties, is produced at the Redkino Experimental Plant in Tver Region. Replacing it with alternatives is not recommended, as the requirements for this type of fuel are highly specific. This fuel is produced catalytically from the hydrocarbon dicyclopentadiene, and the application of the catalyst may involve the use of the cation exchange resin Purolite CT-175, manufactured by the U.S. company Ecolab.
Tall oils are a byproduct of pulp and paper production.
Wear resistance, low-temperature stability, cetane number, conductivity.
pp.27-31, Issue 12, 2007.
Lanthanum and cerium compounds reduce aluminum losses in zeolite-based catalysts, thereby improving catalyst activity and stability. According to Russian scientists, lanthanum helps prevent a reduction in the active surface of alumina-based catalysts. Lanthanum and cerium additives also lower the catalytic cracking temperature for the production of olefins (unsaturated hydrocarbons), enhancing the environmental performance of the process. Other studies by Iranian researchers confirm the effectiveness of lanthanum and cerium additives.
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7718845695
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7701275006
These dates correspond to the year 1402 in the Persian calendar.
Another subsidiary of Maire Tecnimont.
An Italian company specializing in engineering, primarily for the production of hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol.
A Swiss chemical-technology company specializing in large-scale production of ammonia, urea, and nitrogen fertilizers.
A Danish engineering firm that supplies both end-to-end production lines and individual units and consumables.
The removal of paraffins from petroleum products through a catalytic process using hydrogen. Paraffins are hazardous because they can precipitate at low temperatures, potentially causing serious engine damage.
Hydrodearomatization is the conversion of cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons into saturated ones under the action of hydrogen.
Oligomerization is the creation of short polymer fragments.
A Shell subsidiary engaged in catalyst production.
An American corporation that produces technological products for the oil and gas chemical industries.
Axens is a French petrochemical and energy company.
Para-tert-butylphenol is used in the production of special-purpose phenol-formaldehyde resins, which serve as binding components in explosives, rocket propellants, and charge systems. This makes PTBP a critical substance for:
- artillery shells
- aerial bombs
- multiple launch rocket systems, such as Grad and Smerch.
It is also used as a component in heat-resistant, high-endurance materials:
- in missile casings
- in fuzes and detonators
- in highly reliable electronic components for air‑defense systems and drones.
The list of parameters includes composition stability, specific heat of combustion, and specific impulse.
A process in which hydrocarbon chains are converted from linear or lightly branched structures into more highly branched isomers to enhance the desired properties of petroleum products.
The production of shorter hydrocarbons from longer ones.
Exposure of petroleum products to hydrogen in order to remove sulfur from them.

Zircon (SS-N-33) missile test
Phenol-formaldehyde and epoxy resins are used in the production of aircraft and components of weapons and ammunition. Phenol-formaldehyde resins are key to the manufacturing of polymer and composite parts with advanced mechanical, insulating, and thermal properties. Such composites are in high demand in aviation. Phenol-formaldehyde resins are a high-tonnage product with a range of civilian uses. In 2019, they were produced by 15 Russian enterprises. However, one of the key ingredients, para-tert-butylphenol (PTBP), is produced only at the Novokuibyshevsk Plant in Samara Region. Without PTBP, it is impossible to produce phenol-formaldehyde resins, which are used as a binding agent in explosives for artillery shells, bombs, and multiple launch rocket systems, as well as for heat-resistant fuzes and detonators.
Its synthesis requires a catalyst and an ion-exchange resin (a cation exchanger) — either the Russian-made KU-23, or Amberlyst 36 Dry, which is produced by the American company DuPont. However, research by Samara chemists shows that the DuPont cation exchanger is significantly more efficient than the domestic one.
Aramid fibers form the basis of ballistic fabric for body armor. They are also used in drone manufacturing, ballistic textiles, protective helmets, and in the production of aramid laminate, a composite material for armored vehicles. Producing aramid fibers requires auxiliary components such as para-phenylenediamine and N,N-dimethylacetamide, neither of which is produced in Russia. Only one enterprise in the country can produce aramid fibers using high-speed sulfuric-acid technology, and Russia does not manufacture serial equipment for aramid yarn production.
EU sanctions and export-control regulations impose far more extensive restrictions on the supply of physical equipment than on the delivery of chemical components. Around 1000 lines in the dual-use technology classifier of products that cannot be sent to Russia consist of electronics, optics, laser and acoustic technology, cryogenic equipment, magnetometers, radars, semiconductor lithography equipment, metalworking machinery, and bearings. At the same time, the prohibition list includes only around 200 individual chemical substances and only about a dozen groups of substances. The section covering unconditional export restrictions by HS codes blocks supplies of roughly 70 substances and their groups to Russia.
Critical dependence on imported catalysts in petrochemicals
The Russian chemical industry, like other manufacturing industries, has certainly been hit by export restrictions and Western sanctions.
The foundation of organic chemistry is feedstock produced by the petrochemical industry. Hydrotreating removes sulfur and nitrogen compounds from crude oil. Cracking breaks down heavy hydrocarbons (such as fuel oil and gas oil) into lighter ones (like gasoline). Reforming, in addition to producing high-octane fuels, generates aromatic compounds that serve as the basis for organic synthesis.
Almost all petrochemical processes rely on catalysis. Specialists at the oil information agency Devon assess Russia’s dependence on imported catalysts as critical: “By early 2022, total annual catalyst consumption in Russia had reached 20,000 tons, with 70–80% dependent on imports. For certain categories, the dependency reaches up to 100%. Demand for the most sought-after types of catalysts — for catalytic cracking, hydrocracking, and hydrotreating — amounted to 18,000 metric tons, with cracking catalysts accounting for 12,000–12,500 tons.”
Tall oils are a byproduct of pulp and paper production.
Wear resistance, low-temperature stability, cetane number, conductivity.
pp.27-31, Issue 12, 2007.
Lanthanum and cerium compounds reduce aluminum losses in zeolite-based catalysts, thereby improving catalyst activity and stability. According to Russian scientists, lanthanum helps prevent a reduction in the active surface of alumina-based catalysts. Lanthanum and cerium additives also lower the catalytic cracking temperature for the production of olefins (unsaturated hydrocarbons), enhancing the environmental performance of the process. Other studies by Iranian researchers confirm the effectiveness of lanthanum and cerium additives.
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7718845695
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7701275006
These dates correspond to the year 1402 in the Persian calendar.
Another subsidiary of Maire Tecnimont.
An Italian company specializing in engineering, primarily for the production of hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol.
A Swiss chemical-technology company specializing in large-scale production of ammonia, urea, and nitrogen fertilizers.
A Danish engineering firm that supplies both end-to-end production lines and individual units and consumables.
The removal of paraffins from petroleum products through a catalytic process using hydrogen. Paraffins are hazardous because they can precipitate at low temperatures, potentially causing serious engine damage.
Hydrodearomatization is the conversion of cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons into saturated ones under the action of hydrogen.
Oligomerization is the creation of short polymer fragments.
A Shell subsidiary engaged in catalyst production.
An American corporation that produces technological products for the oil and gas chemical industries.
Axens is a French petrochemical and energy company.
Para-tert-butylphenol is used in the production of special-purpose phenol-formaldehyde resins, which serve as binding components in explosives, rocket propellants, and charge systems. This makes PTBP a critical substance for:
- artillery shells
- aerial bombs
- multiple launch rocket systems, such as Grad and Smerch.
It is also used as a component in heat-resistant, high-endurance materials:
- in missile casings
- in fuzes and detonators
- in highly reliable electronic components for air‑defense systems and drones.
The list of parameters includes composition stability, specific heat of combustion, and specific impulse.
A process in which hydrocarbon chains are converted from linear or lightly branched structures into more highly branched isomers to enhance the desired properties of petroleum products.
The production of shorter hydrocarbons from longer ones.
Exposure of petroleum products to hydrogen in order to remove sulfur from them.
As of early 2022, Russia’s dependence on imported catalysts was 70–80%, reaching up to 100% for certain categories
Catalytic hydrogen production is also dependent on imports at a level of 90%.
Zeolites form the basis for a wide range of catalysts. According to the Russian Academy of Sciences, only Y-type and ZSM-5 zeolites are produced in Russia, while other types, which are required in amounts measuring in the hundreds of tons, are imported.
“Another problem is that the petrochemical industry requires a much greater variety of catalysts — over a hundred types. However, demand for each individual catalyst is much smaller than in oil refining, ranging within 50–100 metric tons nationwide. Setting up production for such small volumes is unprofitable for enterprises,” Alexander Noskov, deputy director of the G. K. Boreskov Institute of Catalysis, explained at the start of the full-scale war. “This was attempted in the USSR, when the industry was geared toward self-sufficiency, but after transitioning to a market economy, Russia began sourcing most catalysts for the petrochemical industry abroad.”
Until 2022, Russia's leading brands of imported catalysts were Axens, UPO, and Criterion. Specialists from the Russian Academy of Sciences note that Russia is fully dependent on imports for catalysts used in the hydrotreatment of petroleum products (the removal of sulfur-containing impurities) and for the catalysts needed to produce Arctic-grade diesel fuel.
According to Noskov, “Another vulnerable area in oil refining is catalysts for producing winter and Arctic fuels (with an annual consumption of 200–250 metric tons). These technologies rely on imported catalysts, and their rapid replacement is hardly possible.”
Dependence on imports persists for petrochemical processes such as alkene oligomerization, hydrodearomatization, and hydrodeparaffinization, as well as for producing feedstock for most polymers (except rubber and polyvinyl chloride).
Western equipment for gas chemistry
The situation in gas-chemical production is no better: until very recently, methanol plants producing methanol from methane preferred to use Danish Haldor Topsoe catalysts.
In 2021, the ammonia production lines (and therefore urea and nitric acid production as well) for TogliattiAzot were to be built by the Swiss firm Casale. Those lines were not launched until 2023. Ammonia production capacity was built jointly with KuibyshevAzot by MET Development, a subsidiary of the Italian company Maire Tecnimont, with licensing provided by Stamicarbon. Ammonia and its derivatives are used everywhere, but most notably for the Russian case, it is needed for the production of nitric acid, which is required for almost all explosives.
Catalyst production: capacity fell short
Experts note that “the most acute import substitution challenge for Russia’s oil-refining industry is hydrotreating and hydrocracking catalysts.” State-controlled oil giant Rosneft launched Russia's first hydrocracking catalyst production line in 2022 in Sterlitamak, where the plant’s start-up was reported with fanfare. The line’s purpose is to partially replace imported hydrocracking catalysts.
Since 2019, the Gazpromneft Catalytic Systems plant has been under construction in Omsk. Its planned capacity totals 21,000 metric tons of catalysts per year (4,000 metric tons of hydrotreating catalysts, 15,000 metric tons of catalytic cracking catalysts, and 2,000 metric tons of other varieties).
However, these volumes are barely sufficient to meet domestic demand. As Noskov noted, Russia consumes 3,500–4,000 metric tons of hydrotreating catalysts and 1,000–1,500 metric tons of hydrocracking catalysts per year.
Iranian assistance
As a result, Russia has been forced to turn to friendly countries, such as Iran. From Mar. 21, 2023, to Mar. 20, 2024, Tehran exported 500 metric tons of raw materials for petrochemical catalysts, according to Morteza Shahmirzaei, CEO of Iran’s National Petrochemical Company. Shahmirzaei stated that collaboration with Russia in the field of catalysis had begun as early as March–April 2022.
The Insider analyzed Russian customs data and found the Emirati company Prolab Industries F.Z.C. listed as the manufacturer and exporter of these types of catalysts to Russia. Meanwhile, the suppliers included the intermediary firms Odyssey Shipping Services (UAE), Supplylink (Kyrgyzstan), and Bms Sondaj Makinalari Sanayi Ve Dis Ticaret Ltd Sti (Turkey). Notably, the UAE’s Prolab Industries F.Z.C. does not run any production facilities, potentially indicating a re-export of components from Iran.
According to The Insider’s calculations, in the Persian year 1402 (starting March 2023), Prolab Industries delivered 420 metric tons of substances for producing refining catalysts to Avangard Trans Group LLC and Khimtekh LLC. Customs documents mistakenly list the weight in kilograms instead of tons, but the correct weight can be inferred from the batch price (the market price of lanthanum oxide is around $3,000 per ton, while the imported batches cost a total of $600,000–$800,000). Avangard Trans Group describes itself as a company supplying Gazprom’s oil and gas transport enterprises with spare parts and components.
The chemical was supplied under the trade name “Activator PIXO-QE5” (contains lanthanides). Deliveries have continued into the Persian years 1403–1404 (i.e., from the end of March 2024 to the present).
Compounds of the rare-earth metals lanthanum and cerium, as noted by Iranian petrochemist Sasan Talebnejad, are widely used in catalytic cracking.
The Insider has sent inquiries to Avangard Trans Group and Prolab Industries F.Z.C.
Polymers: no catalysts for polypropylene and polyethylene
In addition to their necessity in fuel production, catalysts are also critical for producing polymers with specific properties.
In 2007, Plastics Magazine noted that “Russia's level of petrochemical development is catastrophically low: the country accounts for only 1.3% of hydrocarbon feedstock processed for polyolefin production. For every ton of oil and gas consumed in Russia, only 3 kg of polyolefins are produced, compared with 15 kg in the U.S., 21 kg in Western Europe, 29 kg in China, and 32 kg in Brazil.”
Since then, the situation has improved little. For example, Lukoil previously purchased catalysts from Texas-based Lummus Technology for the production of urea, polyethylene, and polypropylene.
“Russia's tightest bottlenecks are polyethylene and polypropylene production, which currently totals about 4–5 million metric tons per year. In these processes, the catalyst is single-use and present in millionths within the product itself. For these 4–5 million tons, approximately 100–120 tons of catalyst are needed. If supplies of the required catalyst stop, production will halt within a month. The tire and paint industries could also face catalyst shortages,” Noskov explains.
Tall oils are a byproduct of pulp and paper production.
Wear resistance, low-temperature stability, cetane number, conductivity.
pp.27-31, Issue 12, 2007.
Lanthanum and cerium compounds reduce aluminum losses in zeolite-based catalysts, thereby improving catalyst activity and stability. According to Russian scientists, lanthanum helps prevent a reduction in the active surface of alumina-based catalysts. Lanthanum and cerium additives also lower the catalytic cracking temperature for the production of olefins (unsaturated hydrocarbons), enhancing the environmental performance of the process. Other studies by Iranian researchers confirm the effectiveness of lanthanum and cerium additives.
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7718845695
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7701275006
These dates correspond to the year 1402 in the Persian calendar.
Another subsidiary of Maire Tecnimont.
An Italian company specializing in engineering, primarily for the production of hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol.
A Swiss chemical-technology company specializing in large-scale production of ammonia, urea, and nitrogen fertilizers.
A Danish engineering firm that supplies both end-to-end production lines and individual units and consumables.
The removal of paraffins from petroleum products through a catalytic process using hydrogen. Paraffins are hazardous because they can precipitate at low temperatures, potentially causing serious engine damage.
Hydrodearomatization is the conversion of cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons into saturated ones under the action of hydrogen.
Oligomerization is the creation of short polymer fragments.
A Shell subsidiary engaged in catalyst production.
An American corporation that produces technological products for the oil and gas chemical industries.
Axens is a French petrochemical and energy company.
Para-tert-butylphenol is used in the production of special-purpose phenol-formaldehyde resins, which serve as binding components in explosives, rocket propellants, and charge systems. This makes PTBP a critical substance for:
- artillery shells
- aerial bombs
- multiple launch rocket systems, such as Grad and Smerch.
It is also used as a component in heat-resistant, high-endurance materials:
- in missile casings
- in fuzes and detonators
- in highly reliable electronic components for air‑defense systems and drones.
The list of parameters includes composition stability, specific heat of combustion, and specific impulse.
A process in which hydrocarbon chains are converted from linear or lightly branched structures into more highly branched isomers to enhance the desired properties of petroleum products.
The production of shorter hydrocarbons from longer ones.
Exposure of petroleum products to hydrogen in order to remove sulfur from them.
If supplies of the required catalyst stop, polyethylene and polypropylene production will halt within a month
“We do not have domestic catalysts for ethylene and propylene polymerization yet. They are still being purchased from the West, and the prospects of import substitution remain vague. Some time ago, the Institute of Catalysis of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences developed such a catalyst, but due to lack of demand in Russia, the license was sold to the UAE, which later established production in the U.S.,” notes Vladimir Kapustin, head of the Department of Oil Production and Processing at the Russian University of Oil and Gas.
This year, SIBUR announced plans to build a polymer catalyst plant in Kazan by 2027. For now, however, dependence on foreign catalysts in polymer petrochemistry remains very high.
New industrial complexes for petrochemicals: smuggling or replication
For many years, Russia imported hydrotreating, cracking, and reforming units from South Korea and Italy. Recently though, domestic petrochemical companies have reported several successful installations of new equipment.
Russian companies have successfully replicated some technologies through licensed equipment production. This was the case with the Italian furnace reactor at the hydrogen production unit from Danish Haldor Topsøe during the construction of a new production line at Nizhnekamsk’s Taneko.
The hydrocracking reactor was installed in Ust‑Luga in 2024. In 2022, hydrocracking columns for the Nizhnekamsk facility were ordered from India. In July 2025, TASS reported that Tatneft had launched a second hydrocracking unit at the Taneko refinery.
Cracking towers must withstand not only high pressure and temperature, but also prolonged adverse hydrogen exposure, which makes the steel brittle. This is such a complex and hard-to-replicate process for Russian petrochemicals that replacing a failed unit could take years. Without fully operational cracking, a refinery is unable to produce high-octane fuel at its design capacity.
Low-volume chemicals are more dependent on imports than bulk chemicals
In 2022, Salavat Aminev, vice president of the Russian Union of Chemists, stated: “Low-volume chemicals are the Achilles’ heel of Russia’s chemical industry. Almost all key sectors depend on low-volume chemical products, and involving specialists from ‘unfriendly countries’ in developing measures to further this critically important sector — especially when there are Russian industry experts with the necessary skills and experience — is a strange choice.”
In March 2024, industry press listed the following reasons for the dire state of low-volume chemicals: “In the post-Soviet period, the development of low-volume chemical production in Russia received virtually no attention. As a result, a significant number of Soviet-era enterprises and facilities producing low-volume chemical products ceased to exist.” The output of low-volume chemicals in Russia has shrunk to a fraction of what it was, and the lion’s share of demand for these products is now met through imports.
“Russia has two producers of 2-ethylhexanoic acid, but their product is of mediocre quality,” chemist Andrei Musin says. “It contains impurities that form a black residue. In antifreeze, this residue remains on engine parts and can interfere with their operation. Alkyd enamels also turn yellow due to impurities, which is especially noticeable on white paint and exterior facades. To avoid such side effects, pure acid is needed, and no one in Russia currently produces it.”
Fuel additives: no domestic antistatic agents or additives
For fuel to achieve the desired properties across key parameters, it must not only consist of hydrocarbons of specific fractions, but also contain additives.
Scientists from the Gubkin Institute and Gazpromneft concluded that, as of 2021, the market for depressant and dispersant additives was supplied by imports at a level of 95%. These additives make diesel fuel “freeze-resistant” even under extreme Arctic conditions. Among the reasons for such a high share of imports are the absence in Russia of high-pressure reactors and the synthesis technology for these additives based on ethylene and vinyl acetate.
In the wear‑resistant additives market, Russia supplied only 30% of its needs (also as of 2021). Even when additives are produced domestically, they rely on high-quality imported tall oils. Attempts to replace them with fatty acids from vegetable oils compromise the quality.
Russia has no domestic production of ashless antistatic additives. During pumping or mixing, fuel layers can rub against each other and become electrically charged, which hinders the rapid loading of tankers. Antistatic additives prevent fuel from becoming electrified.
Multifunctional additives are needed, in particular, to protect against corrosion and the formation of resin particles in fuel. They also reduce engine friction. As of 2021, Russia also imported 95% of its multifunctional additives. Attempts to establish domestic production have been hindered both by the lack of technology and by the insufficient availability of high-quality olefins.
Suppliers of chemical equipment and catalysts
As of 2021, the top 20 manufacturers whose catalysts were supplied to Russia were companies from Europe, Japan, and the U.S.
Tall oils are a byproduct of pulp and paper production.
Wear resistance, low-temperature stability, cetane number, conductivity.
pp.27-31, Issue 12, 2007.
Lanthanum and cerium compounds reduce aluminum losses in zeolite-based catalysts, thereby improving catalyst activity and stability. According to Russian scientists, lanthanum helps prevent a reduction in the active surface of alumina-based catalysts. Lanthanum and cerium additives also lower the catalytic cracking temperature for the production of olefins (unsaturated hydrocarbons), enhancing the environmental performance of the process. Other studies by Iranian researchers confirm the effectiveness of lanthanum and cerium additives.
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7718845695
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7701275006
These dates correspond to the year 1402 in the Persian calendar.
Another subsidiary of Maire Tecnimont.
An Italian company specializing in engineering, primarily for the production of hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol.
A Swiss chemical-technology company specializing in large-scale production of ammonia, urea, and nitrogen fertilizers.
A Danish engineering firm that supplies both end-to-end production lines and individual units and consumables.
The removal of paraffins from petroleum products through a catalytic process using hydrogen. Paraffins are hazardous because they can precipitate at low temperatures, potentially causing serious engine damage.
Hydrodearomatization is the conversion of cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons into saturated ones under the action of hydrogen.
Oligomerization is the creation of short polymer fragments.
A Shell subsidiary engaged in catalyst production.
An American corporation that produces technological products for the oil and gas chemical industries.
Axens is a French petrochemical and energy company.
Para-tert-butylphenol is used in the production of special-purpose phenol-formaldehyde resins, which serve as binding components in explosives, rocket propellants, and charge systems. This makes PTBP a critical substance for:
- artillery shells
- aerial bombs
- multiple launch rocket systems, such as Grad and Smerch.
It is also used as a component in heat-resistant, high-endurance materials:
- in missile casings
- in fuzes and detonators
- in highly reliable electronic components for air‑defense systems and drones.
The list of parameters includes composition stability, specific heat of combustion, and specific impulse.
A process in which hydrocarbon chains are converted from linear or lightly branched structures into more highly branched isomers to enhance the desired properties of petroleum products.
The production of shorter hydrocarbons from longer ones.
Exposure of petroleum products to hydrogen in order to remove sulfur from them.
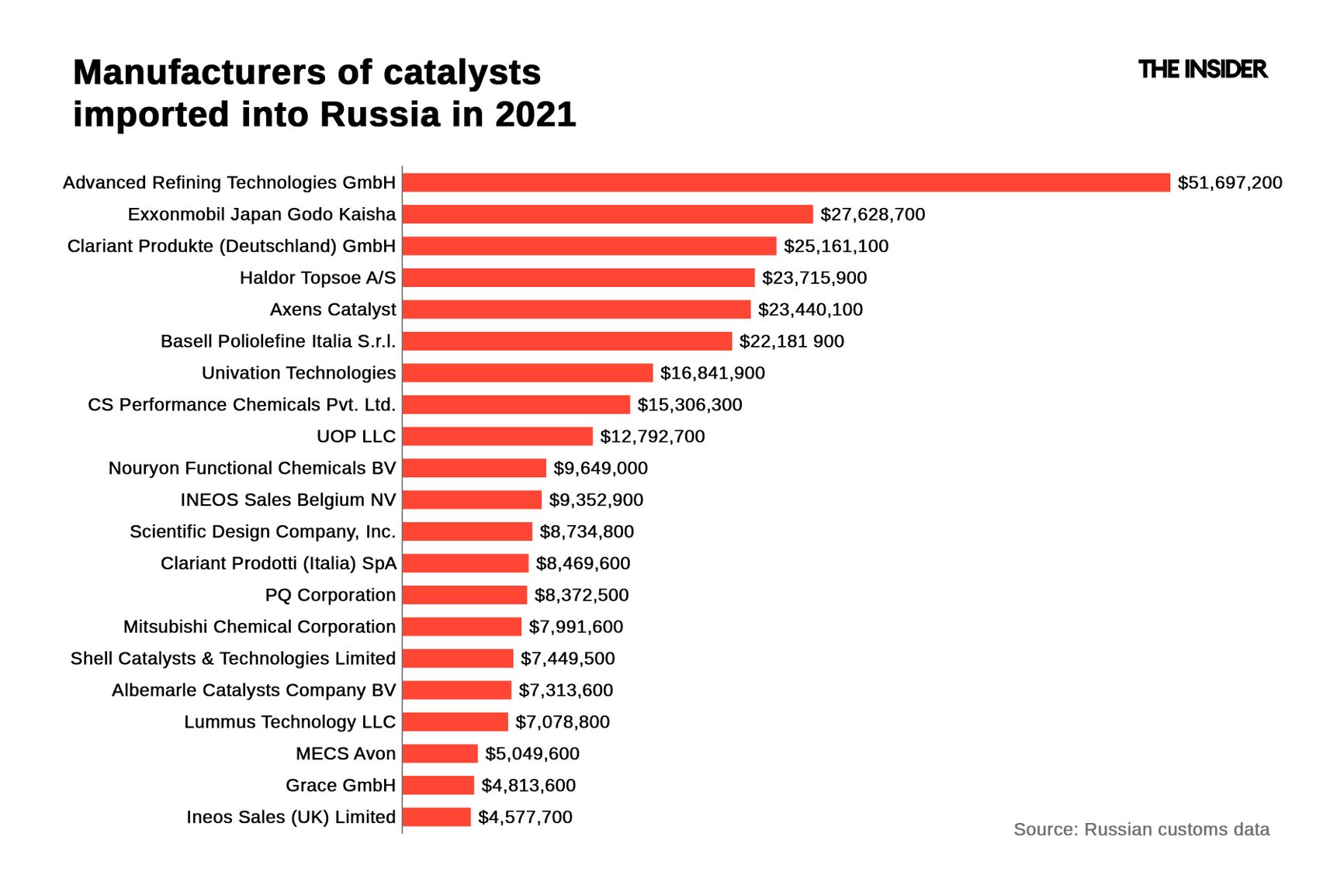
Catalyst manufacturers whose products were imported into Russia in 2021
However, by 2024 the situation had changed radically. Not a single Western company was listed among the Russian market leaders.
Tall oils are a byproduct of pulp and paper production.
Wear resistance, low-temperature stability, cetane number, conductivity.
pp.27-31, Issue 12, 2007.
Lanthanum and cerium compounds reduce aluminum losses in zeolite-based catalysts, thereby improving catalyst activity and stability. According to Russian scientists, lanthanum helps prevent a reduction in the active surface of alumina-based catalysts. Lanthanum and cerium additives also lower the catalytic cracking temperature for the production of olefins (unsaturated hydrocarbons), enhancing the environmental performance of the process. Other studies by Iranian researchers confirm the effectiveness of lanthanum and cerium additives.
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7718845695
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7701275006
These dates correspond to the year 1402 in the Persian calendar.
Another subsidiary of Maire Tecnimont.
An Italian company specializing in engineering, primarily for the production of hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol.
A Swiss chemical-technology company specializing in large-scale production of ammonia, urea, and nitrogen fertilizers.
A Danish engineering firm that supplies both end-to-end production lines and individual units and consumables.
The removal of paraffins from petroleum products through a catalytic process using hydrogen. Paraffins are hazardous because they can precipitate at low temperatures, potentially causing serious engine damage.
Hydrodearomatization is the conversion of cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons into saturated ones under the action of hydrogen.
Oligomerization is the creation of short polymer fragments.
A Shell subsidiary engaged in catalyst production.
An American corporation that produces technological products for the oil and gas chemical industries.
Axens is a French petrochemical and energy company.
Para-tert-butylphenol is used in the production of special-purpose phenol-formaldehyde resins, which serve as binding components in explosives, rocket propellants, and charge systems. This makes PTBP a critical substance for:
- artillery shells
- aerial bombs
- multiple launch rocket systems, such as Grad and Smerch.
It is also used as a component in heat-resistant, high-endurance materials:
- in missile casings
- in fuzes and detonators
- in highly reliable electronic components for air‑defense systems and drones.
The list of parameters includes composition stability, specific heat of combustion, and specific impulse.
A process in which hydrocarbon chains are converted from linear or lightly branched structures into more highly branched isomers to enhance the desired properties of petroleum products.
The production of shorter hydrocarbons from longer ones.
Exposure of petroleum products to hydrogen in order to remove sulfur from them.
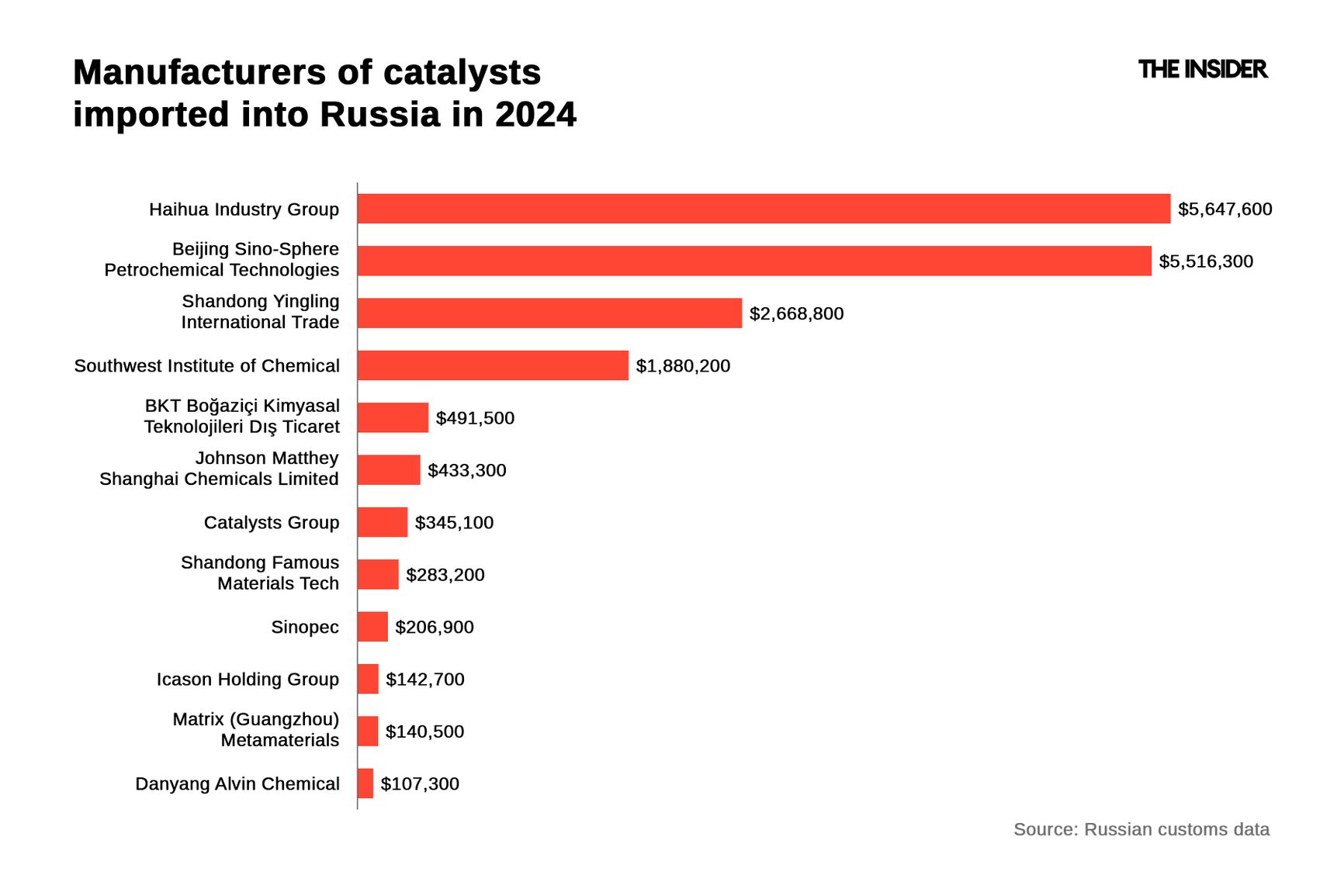
Catalyst manufacturers whose products were imported into Russia in 2024
Russia's volume of catalyst imports in 2024, according to Russian customs data, was around $20 million — significantly lower than in 2021 (around $450 million). Both importers and manufacturers were almost exclusively Chinese.
Tall oils are a byproduct of pulp and paper production.
Wear resistance, low-temperature stability, cetane number, conductivity.
pp.27-31, Issue 12, 2007.
Lanthanum and cerium compounds reduce aluminum losses in zeolite-based catalysts, thereby improving catalyst activity and stability. According to Russian scientists, lanthanum helps prevent a reduction in the active surface of alumina-based catalysts. Lanthanum and cerium additives also lower the catalytic cracking temperature for the production of olefins (unsaturated hydrocarbons), enhancing the environmental performance of the process. Other studies by Iranian researchers confirm the effectiveness of lanthanum and cerium additives.
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7718845695
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7701275006
These dates correspond to the year 1402 in the Persian calendar.
Another subsidiary of Maire Tecnimont.
An Italian company specializing in engineering, primarily for the production of hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol.
A Swiss chemical-technology company specializing in large-scale production of ammonia, urea, and nitrogen fertilizers.
A Danish engineering firm that supplies both end-to-end production lines and individual units and consumables.
The removal of paraffins from petroleum products through a catalytic process using hydrogen. Paraffins are hazardous because they can precipitate at low temperatures, potentially causing serious engine damage.
Hydrodearomatization is the conversion of cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons into saturated ones under the action of hydrogen.
Oligomerization is the creation of short polymer fragments.
A Shell subsidiary engaged in catalyst production.
An American corporation that produces technological products for the oil and gas chemical industries.
Axens is a French petrochemical and energy company.
Para-tert-butylphenol is used in the production of special-purpose phenol-formaldehyde resins, which serve as binding components in explosives, rocket propellants, and charge systems. This makes PTBP a critical substance for:
- artillery shells
- aerial bombs
- multiple launch rocket systems, such as Grad and Smerch.
It is also used as a component in heat-resistant, high-endurance materials:
- in missile casings
- in fuzes and detonators
- in highly reliable electronic components for air‑defense systems and drones.
The list of parameters includes composition stability, specific heat of combustion, and specific impulse.
A process in which hydrocarbon chains are converted from linear or lightly branched structures into more highly branched isomers to enhance the desired properties of petroleum products.
The production of shorter hydrocarbons from longer ones.
Exposure of petroleum products to hydrogen in order to remove sulfur from them.
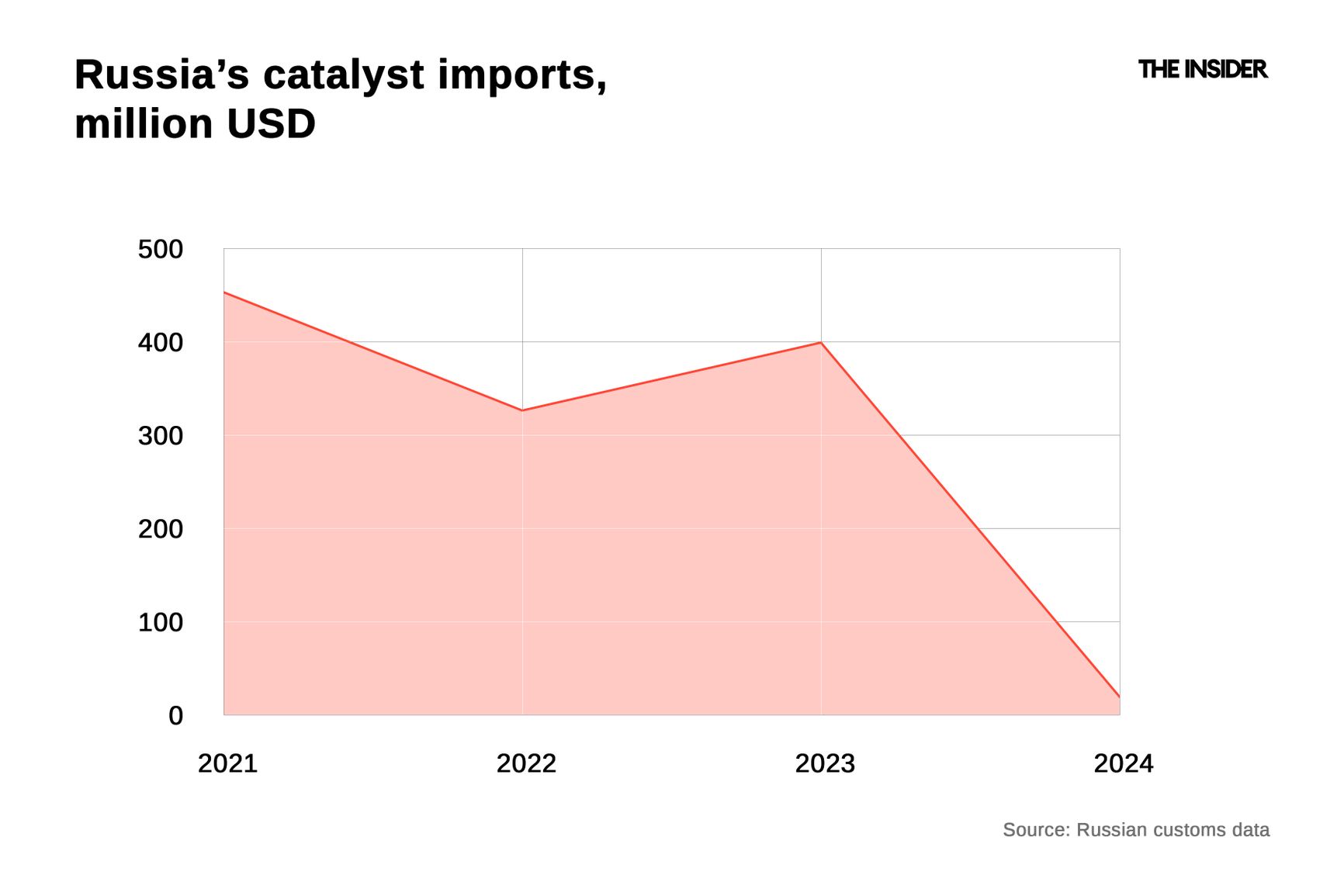
Catalyst imports to Russia
In 2025, China has supplied almost all of the equipment for Russian chemical production. The majority of the equipment (around 20 reactors) was manufactured in China. A single reactor for alkyd resin synthesis was originally made in Germany by Fluid Solutions GmbH, and a few more were made in India.
Where the Russian chemical industry stands in 2025
Over the past 30 years, Russia has struggled to develop its own chemical production technologies beyond the sphere of basic oil distillation. Most of its research has been confined to labs at universities or research institutes.
Now, under the pressure of international sanctions, Russian authorities are trying to establish domestic production of catalysts and polymers. However, hardly any of these can be produced without imported equipment.
So far, Russia has failed to close the gap in the key segment: supplying the petrochemical industry with catalysts for cracking, reforming, aromatization, and hydrotreating, as well as for fuel additives, critical polymer components, fibers, and resins. Instead, it continues to rely on assistance from China, India, and Iran.
Tall oils are a byproduct of pulp and paper production.
Wear resistance, low-temperature stability, cetane number, conductivity.
pp.27-31, Issue 12, 2007.
Lanthanum and cerium compounds reduce aluminum losses in zeolite-based catalysts, thereby improving catalyst activity and stability. According to Russian scientists, lanthanum helps prevent a reduction in the active surface of alumina-based catalysts. Lanthanum and cerium additives also lower the catalytic cracking temperature for the production of olefins (unsaturated hydrocarbons), enhancing the environmental performance of the process. Other studies by Iranian researchers confirm the effectiveness of lanthanum and cerium additives.
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7718845695
Taxpayer Identification Number (INN) 7701275006
These dates correspond to the year 1402 in the Persian calendar.
Another subsidiary of Maire Tecnimont.
An Italian company specializing in engineering, primarily for the production of hydrogen, ammonia, and methanol.
A Swiss chemical-technology company specializing in large-scale production of ammonia, urea, and nitrogen fertilizers.
A Danish engineering firm that supplies both end-to-end production lines and individual units and consumables.
The removal of paraffins from petroleum products through a catalytic process using hydrogen. Paraffins are hazardous because they can precipitate at low temperatures, potentially causing serious engine damage.
Hydrodearomatization is the conversion of cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons into saturated ones under the action of hydrogen.
Oligomerization is the creation of short polymer fragments.
A Shell subsidiary engaged in catalyst production.
An American corporation that produces technological products for the oil and gas chemical industries.
Axens is a French petrochemical and energy company.
Para-tert-butylphenol is used in the production of special-purpose phenol-formaldehyde resins, which serve as binding components in explosives, rocket propellants, and charge systems. This makes PTBP a critical substance for:
- artillery shells
- aerial bombs
- multiple launch rocket systems, such as Grad and Smerch.
It is also used as a component in heat-resistant, high-endurance materials:
- in missile casings
- in fuzes and detonators
- in highly reliable electronic components for air‑defense systems and drones.
The list of parameters includes composition stability, specific heat of combustion, and specific impulse.
A process in which hydrocarbon chains are converted from linear or lightly branched structures into more highly branched isomers to enhance the desired properties of petroleum products.
The production of shorter hydrocarbons from longer ones.
Exposure of petroleum products to hydrogen in order to remove sulfur from them.