

Western sanctions typically target foreign exporters supplying sanctioned goods to Russia, along with the Russian importers that use those goods in military production. Yet an important link remains in the shadows: customs brokers who make this trade possible. The Insider has identified 30 leading Russian brokerage firms specializing in the trade of sanctioned products. Many of them openly advertise their services.
Content
Who are customs brokers?
In their own words
Western goods for Putin’s war machine
Who are customs brokers?
Anyone who has dealt with customs clearance in Russia knows how much money and effort it can take for a business to import goods legally. As a result, customs brokers who help prepare the necessary documents and resolve unexpected issues during the importation process earn millions of dollars.
In 2024, Russian customs brokers helped clear sanctioned goods worth more than $4.4 billion. This figure applies only to products that both the EU and the U.S. had prohibited from being exported to Russia and which were produced in countries supporting Ukraine. Only shipments valued at more than $20,000 were counted in the figure, meaning the true total is markedly higher.
For example, customs broker Dzhamal Davitashvili works with numerous importing companies and, in 2024 alone, filed more than 25,000 customs declarations, covering $600 million worth of goods that were cleared and imported into Russia. These include machinery, electronics, and various equipment worth tens of millions of dollars. In the declarations filed by Davitashvili, the most frequently listed item is “multilayer printed circuits.” In addition to handling hardware, Davitashvili also helped process approximately 30 tons of brassieres worth around $5 million.
The infographic below shows 30 leading Russian brokerage firms that helped companies clear imports of foreign-made sanctioned equipment (restricted by both the U.S. and the EU).
The main function of a steam reforming furnace is to produce hydrogen, which is then used in various industrial processes such as ammonia production, methanol production, and petroleum hydroprocessing.
You may find an example in a Habr article about an attempt to clear a 3D printer through customs to import it into Russia.
Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, the United Kingdom, Hungary, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Ireland, Iceland, Spain, Italy, Canada, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Malta, Monaco, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, the Republic of Korea, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, the United States, Finland, France, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Switzerland, Sweden, Estonia, Japan, Taiwan.
The lists of codes are provided in the following documents: for the European Union, in Annexes VII and XXIII of Directive 833/2014 as of December 2023; for the United States, in Supplement No. 4 to §746.5(a)(1)(ii) of the U.S. Export Administration Regulations as of January 1, 2024.
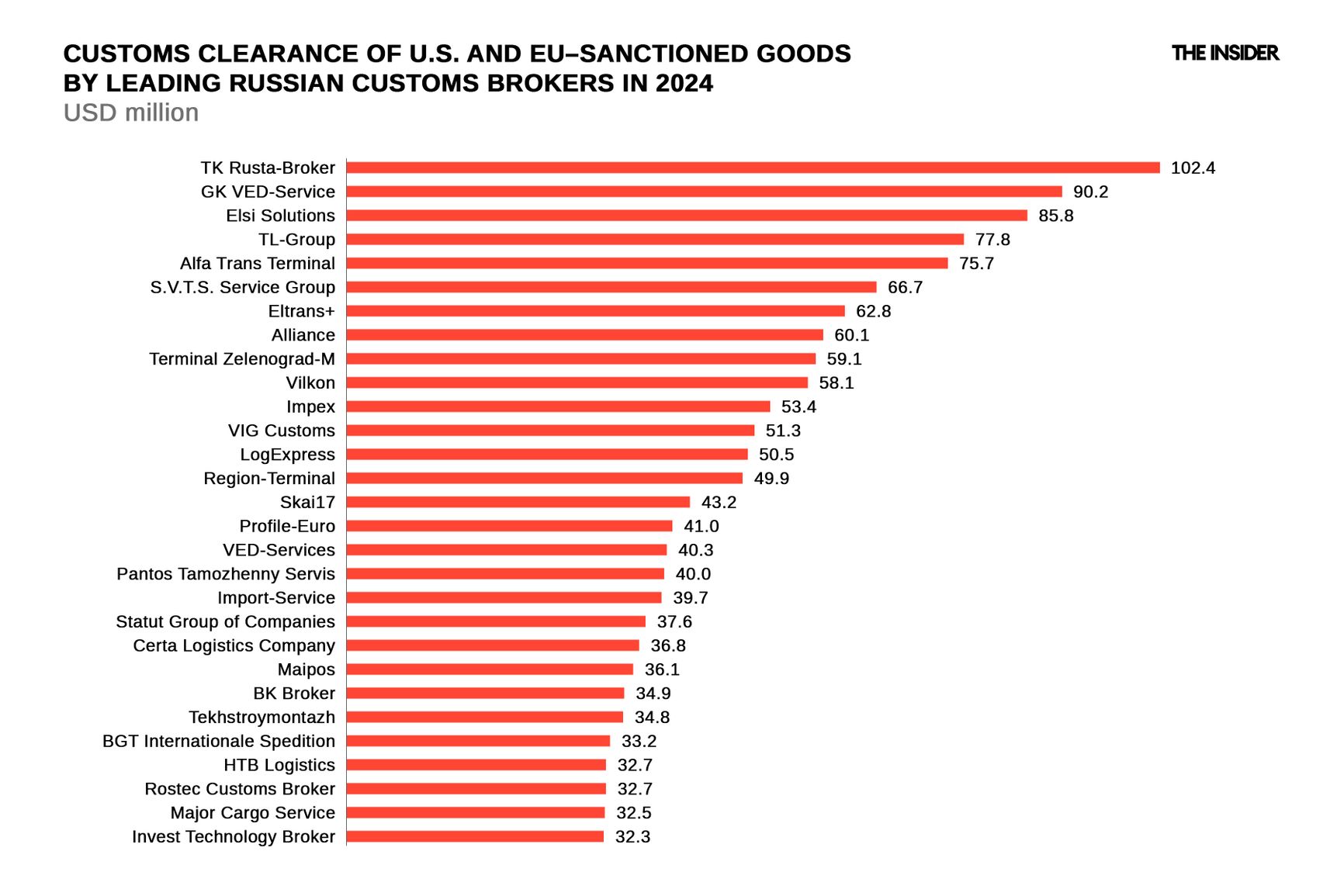
One individual — the person who fills out customs declarations — can work with multiple brokerage firms, sometimes without listing them in the documents. The infographic shows statistics only for the companies specified in the relevant fields of the declarations. Statistics on individuals who fill out the forms are not provided here.
See the full list of brokers with an annual transaction volume exceeding $10 million here.
Among the importers that used these brokers’ services was the company I Machine, which supplied Taiwanese machinery.
See the full list of customs brokers’ clients here.
In their own words
In their advertising, customs brokers openly promise to help clients circumvent sanctions — and even reveal the schemes they use to do so.
Baltic Logistic Service (BLS) advertises its services in a website section titled “Customs clearance and delivery of goods from EU countries to Russia under the condition of sanctions.” An entry titled “How to circumvent EU sanctions using special logistics and payment schemes” lays out how this is done: “Take a Russian enterprise that uses German generators in its products. If the generator supplier in Germany refuses to sell its goods to Russia, citing EU sanctions, our partner countries enter the supply chain — such as Serbia, which is not a member of the EU. Serbia buys generators in Germany and sends them to Russia.”
Another broker, 1Kargo operator, promises: “Dear partners! We locate, purchase, and deliver products from abroad, bypassing sanctions. [We offer] full support. Everything is official. Customs clearance, payments to foreign partners, favorable terms for the delivery of sanctioned goods.”
The main function of a steam reforming furnace is to produce hydrogen, which is then used in various industrial processes such as ammonia production, methanol production, and petroleum hydroprocessing.
You may find an example in a Habr article about an attempt to clear a 3D printer through customs to import it into Russia.
Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, the United Kingdom, Hungary, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Ireland, Iceland, Spain, Italy, Canada, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Malta, Monaco, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, the Republic of Korea, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, the United States, Finland, France, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Switzerland, Sweden, Estonia, Japan, Taiwan.
The lists of codes are provided in the following documents: for the European Union, in Annexes VII and XXIII of Directive 833/2014 as of December 2023; for the United States, in Supplement No. 4 to §746.5(a)(1)(ii) of the U.S. Export Administration Regulations as of January 1, 2024.

Advertisement of products that were imported in violation of sanctions on the 1Kargo website
ITB openly states on its corporate website: “The ITB Group of Companies imports goods through the ‘parallel import’ mechanism on behalf of our clients.”
The website of Sokoltrade reads: “We offer payment agent services: we select a payment agent, approve and sign the contract. You make payment for the goods to the agent, who transfers the funds to the supplier in Europe, China, or another country within 3–4 business days.”
Any major Russian broker transporting technically complex goods is likely involved in moving equipment subject to EU or U.S. sanctions.
Western goods for Putin’s war machine
While the brokers handling the paperwork and the Russian buyers utilizing sanctioned goods remain difficult to track, the major Western corporations whose goods are processed by these brokers are publicly known. The most notable among them are shown in the infographic, matched with the amounts Russian buyers spent on their purchases of sanctioned products.
The main function of a steam reforming furnace is to produce hydrogen, which is then used in various industrial processes such as ammonia production, methanol production, and petroleum hydroprocessing.
You may find an example in a Habr article about an attempt to clear a 3D printer through customs to import it into Russia.
Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, the United Kingdom, Hungary, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Ireland, Iceland, Spain, Italy, Canada, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Malta, Monaco, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, the Republic of Korea, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, the United States, Finland, France, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Switzerland, Sweden, Estonia, Japan, Taiwan.
The lists of codes are provided in the following documents: for the European Union, in Annexes VII and XXIII of Directive 833/2014 as of December 2023; for the United States, in Supplement No. 4 to §746.5(a)(1)(ii) of the U.S. Export Administration Regulations as of January 1, 2024.
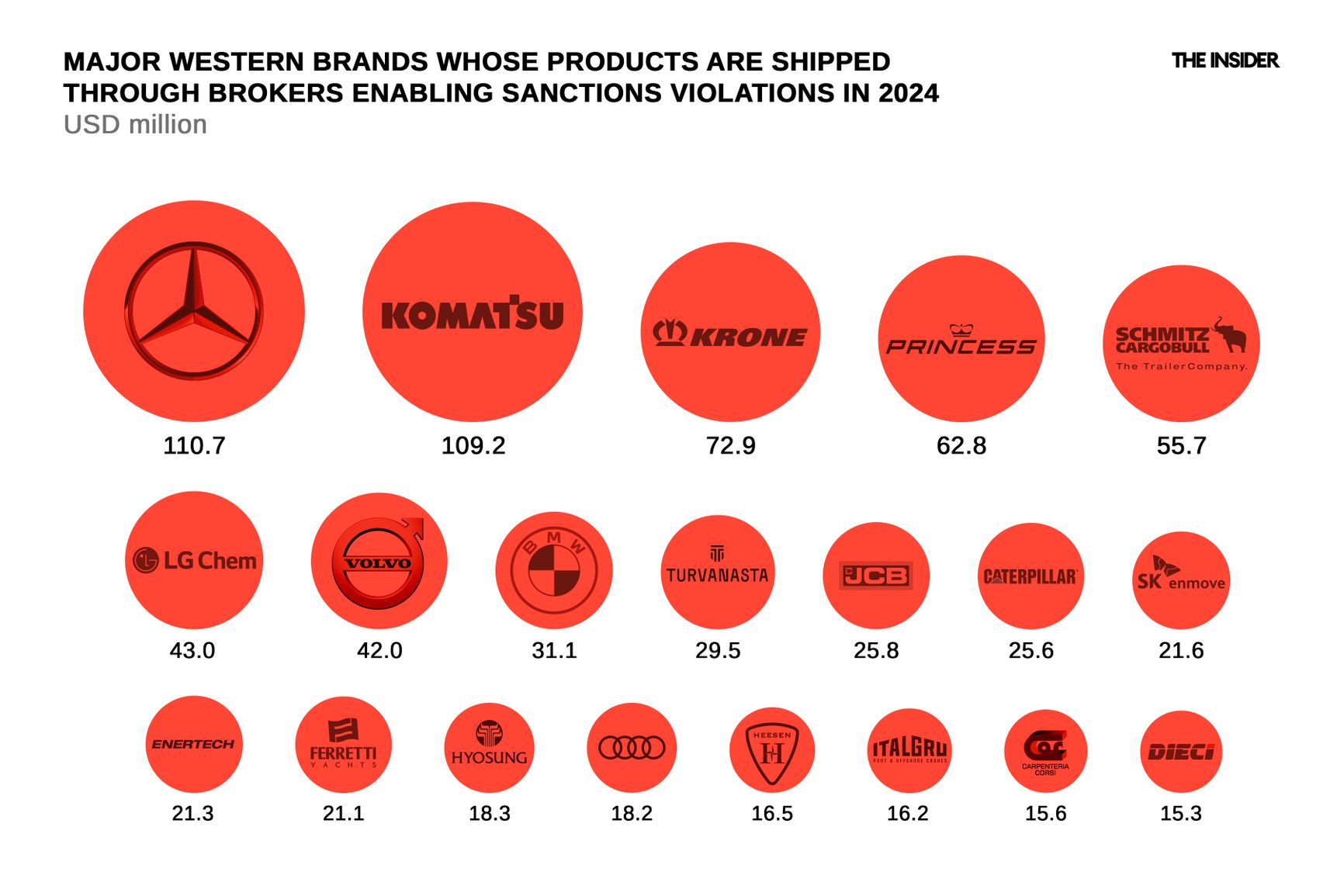
One notable example involves the Korean company Demsko, which produces metal-cutting equipment. In 2025, a company named “LLC Demsko Equipment Plant” was certified in Russia. Judging by the absence of lawsuits in Russian courts from the Koreans over the appropriation of its brand name, the Korean company seems not to object to the situation. Meanwhile, LLC Tamozhenny Broker has cleared $16.9 million worth of Korean-made Demsko equipment through customs.
The equipment — machines vital for the production of rolled steel — was intended for the Magnitogorsk Iron and Steel Works, which produces high-strength steels much needed for the construction of naval vessels.
The Italian company Kirchner Italia S.P.A. produces steam reforming furnaces for oil refining, popular among Russian chemical companies. For instance, the steam reforming furnaces at Shchekinoazot’s plants, which produce ammonia, hexamine, and methanol, are Kirchner units. Kirchner equipment continues to be widely advertised in Russia.
In 2024, LLC GK VED-Service acted as a broker for over $12 million worth of Kirchner products. The broker cleared a steam superheater and a preheater for the prereforming reactor used in methanol production at the Nakhodka Mineral Fertilizer Plant.
The main function of a steam reforming furnace is to produce hydrogen, which is then used in various industrial processes such as ammonia production, methanol production, and petroleum hydroprocessing.
You may find an example in a Habr article about an attempt to clear a 3D printer through customs to import it into Russia.
Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, the United Kingdom, Hungary, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Ireland, Iceland, Spain, Italy, Canada, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Malta, Monaco, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, the Republic of Korea, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, the United States, Finland, France, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Switzerland, Sweden, Estonia, Japan, Taiwan.
The lists of codes are provided in the following documents: for the European Union, in Annexes VII and XXIII of Directive 833/2014 as of December 2023; for the United States, in Supplement No. 4 to §746.5(a)(1)(ii) of the U.S. Export Administration Regulations as of January 1, 2024.
Half of all goods cleared by brokers (in terms of monetary value) passed through just 60 brokerage firms
The German company Rohde & Schwarz produces frequency generators, oscilloscopes, and other complex radio-electronic equipment that are in demand among both military and civilian users. The Insider previously reported on the possible role of Rohde & Schwarz oscilloscopes in the development of Russian electronic warfare systems. LLC Invest Technology Broker cleared more Rohde & Schwarz devices than any other company in Russia.
Overall, half of all goods cleared by brokers (in terms of monetary value) passed through just 60 brokerage firms. However, unlike arms manufacturers and other industrial companies, the brokers themselves have never been at significant risk of falling under sanctions, as they are not direct participants in the transaction. As a result, they continue to operate unimpeded.
The main function of a steam reforming furnace is to produce hydrogen, which is then used in various industrial processes such as ammonia production, methanol production, and petroleum hydroprocessing.
You may find an example in a Habr article about an attempt to clear a 3D printer through customs to import it into Russia.
Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, the United Kingdom, Hungary, Germany, Greece, Denmark, Ireland, Iceland, Spain, Italy, Canada, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Malta, Monaco, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, the Republic of Korea, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, the United States, Finland, France, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Switzerland, Sweden, Estonia, Japan, Taiwan.
The lists of codes are provided in the following documents: for the European Union, in Annexes VII and XXIII of Directive 833/2014 as of December 2023; for the United States, in Supplement No. 4 to §746.5(a)(1)(ii) of the U.S. Export Administration Regulations as of January 1, 2024.